- What is Radar Relay?
- How does the Radar Relay decentralized exchange work?
- How is Radar Relay different?
- When was Radar Relay formed?
- How does Radar Relay make money?
- Additional Resources
The Radar Relay decentralized exchange enables peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies. Technically, it competes with first-generation decentralized exchanges like the OasisDEX, EtherDelta/ForkDelta, IDEX, and Kyber. However, Radar Relay not only outperforms them on a 24-hour trading volume basis. It also effectively competes with established centralized exchanges, like the UK-based CEX.IO in terms of trading volume. This is no small feat for a service still in beta.

Compared to setting up an account at a centralized exchange, it takes fewer steps to start trading with Radar Relay. While Radar Relay may not be as fast as centralized exchanges, it is faster than first-generation decentralized exchanges that have the burden of executing everything on the blockchain.
This Radar Relay guide covers:
- What is Radar Relay?
- How does the Radar Relay decentralized exchange work?
- How is Radar Relay different?
- When was Radar Relay formed?
- How does Radar Relay make money?
- Additional Resources
Radar Relay Key Details
Exchange Classification: Decentralized Modular Trade Network
Open Order Protocol: 0x Order Schema
Ledger Support: Yes
What is Radar Relay?
Radar Relay is a DApp, or decentralized application, designed for wallet-to-wallet trading of cryptocurrencies. Unlike Coinbase, Bitstamp, and other centralized cryptocurrency exchanges, the Radar Relay decentralized exchange does not require you to establish an account. With Radar Relay, you can securely trade tokens without having to share your name, address, and other personal information. Additionally, it has no lockup period or fees for deposits and withdrawals. Like DDEX, the Radar Relay decentralized exchange not only improves security, but also saves time and money. Unfortunately, the Radar Relay service is a bit on the pricey side and can only be used for trading ERC-20 tokens.

How does the Radar Relay decentralized exchange work?
To use the Radar Relay decentralized exchange, you may interface with the website, or trade programmatically using the API. Either way, you essentially use your wallet to place an order. All Radar Relay does is broadcast that order, find a match, and disseminate that information to the Ethereum blockchain via the 0x protocol. The 0x protocol then uses smart contracts to complete the order on the blockchain.
To be precise, Radar Relay is a relayer. Relayers share liquidity information. Liquidity information is essentially information about somebody’s intention to trade one asset for another. Relayers basically craft an order book from cryptographically signed messages from liquidity providers. A liquidity provider, or market maker, is simply any trader signaling an intention to exchange a specific quantity of one asset for another at a specific price during a specified period. On Radar Relay, that period can be an hour, a day, a week, or a month.
The instructions the liquidity provider issues to the relayer are called orders. On Radar Relay, liquidity providers have two options:
- Place a limit order to purchase a quantity of one asset for a specific quantity of another (bid price).
- Place a limit order to sell a quantity of one asset for a specific quantity of another (ask price).
Later on, a liquidity taker, or taker, goes straight to the order book and agrees to do the trade under the conditions specified by the maker. The 0x protocol handles everything from there to fill the order. In essence, 0x creates a smart contract and settles the order on the blockchain.
How is Radar Relay different?
Radar Relay uses a different trust model. According to the Radar Relay marketing materials, Radar Relay is a modular trade network. This is just a fancy way of saying that they are different from the first iteration of decentralized exchanges. What they really mean by that is relayers can share order books and plug into each other to create larger liquidity pools since the 0x protocol handles order settlement. This was not possible on the first generation of decentralized exchanges like EtherDelta. However, it is possible on the Radar Relay decentralized exchange because 0x is an open protocol and relayers only share liquidity information. Consequently, relayers are free to work with each other.
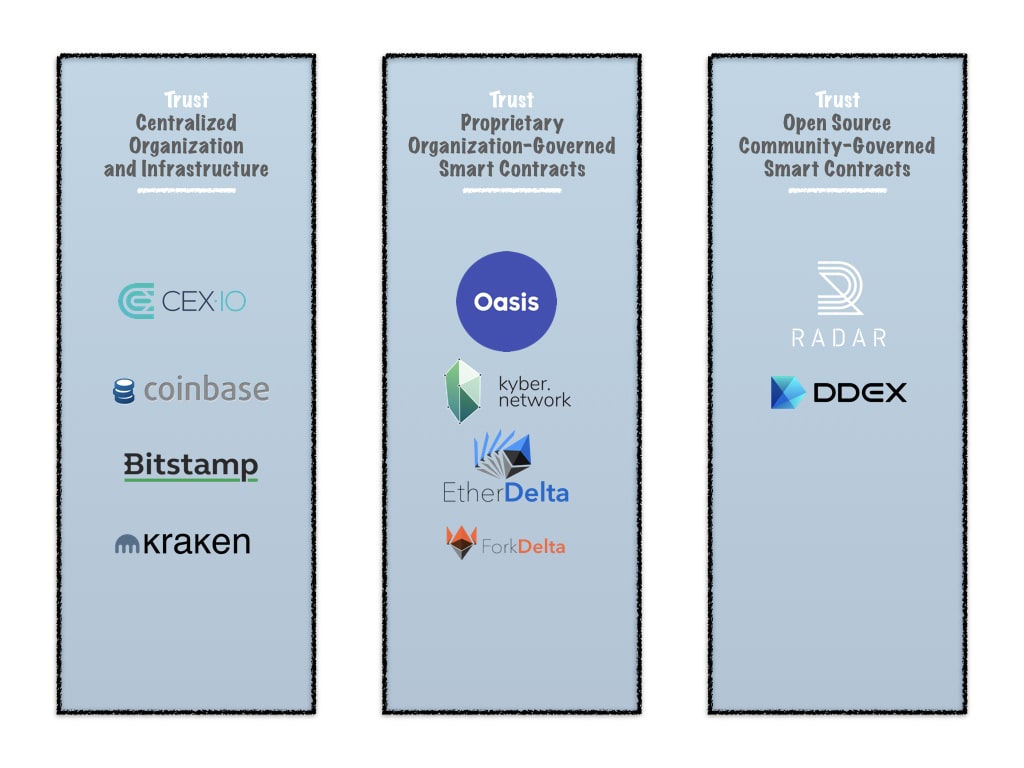
Traditionally, decentralized exchanges used proprietary interfaces and smart contracts to enable trades using either MetaMask or Ledger wallets. On EtherDelta, IDEX, and other first-generation decentralized exchanges, where smart contracts broadcast order information to the blockchain, there was no way to share liquidity because the interfaces were proprietary.
Radar Relay leverages the 0x protocol to speed up the propagation of order information. More importantly, from an interoperation perspective, it leaves the development and governance of order settlement smart contract protocols to a global community of programmers and traders.
When was Radar Relay formed?
The Radar Relay Beta App launched in August 2017. Alan Curtis (CEO), Mike Roth (CTO), Brandon Arthur Roth (CCO), and Devin Eldridge (COO) lead the project. The team received early backing from Blockchain Capital in December 2017. Batshit Crazy Ventures, Collaborative Fund, Digital Currency Group, Kindred Ventures, Kokopelli Capital, Notation Capital, Reciprocal Ventures, Sparkland Capital, V1.VC also participated in the seed round.

How does Radar Relay make money?
Exchanges typically make money by charging fees. Back in August 2017, Radar Relay announced plans to charge maker/taker fees of 0.45%/0.70%. Fees were payable in terms of ZRX tokens. Fees were payable when orders were settled on the Ethereum blockchain for providing the service of hosting and facilitating orders.
Radar Relay implements fee abstraction. Thanks to fee abstraction, traders wouldn’t even know that they are using ZRX tokens to pay transaction fees. That notwithstanding, since November 2017 the Radar Relay decentralized exchange halted charging transaction fees and has seen tremendous success.
Trading volumes highlight Radar Relay’s success. However, it is uncertain that Radar Relay will be able to sustain this momentum when transaction fees are re-introduced. Especially since there are competitors like AirSwap that have business models that don’t depend on transaction fees.
Additional Resources
[thrive_leads id=’5219′]
Never Miss Another Opportunity! Get hand selected news & info from our Crypto Experts so you can make educated, informed decisions that directly affect your crypto profits. Subscribe to CoinCentral free newsletter now.